Architecture
Understand the architecture of the Stacks Blockchain API.
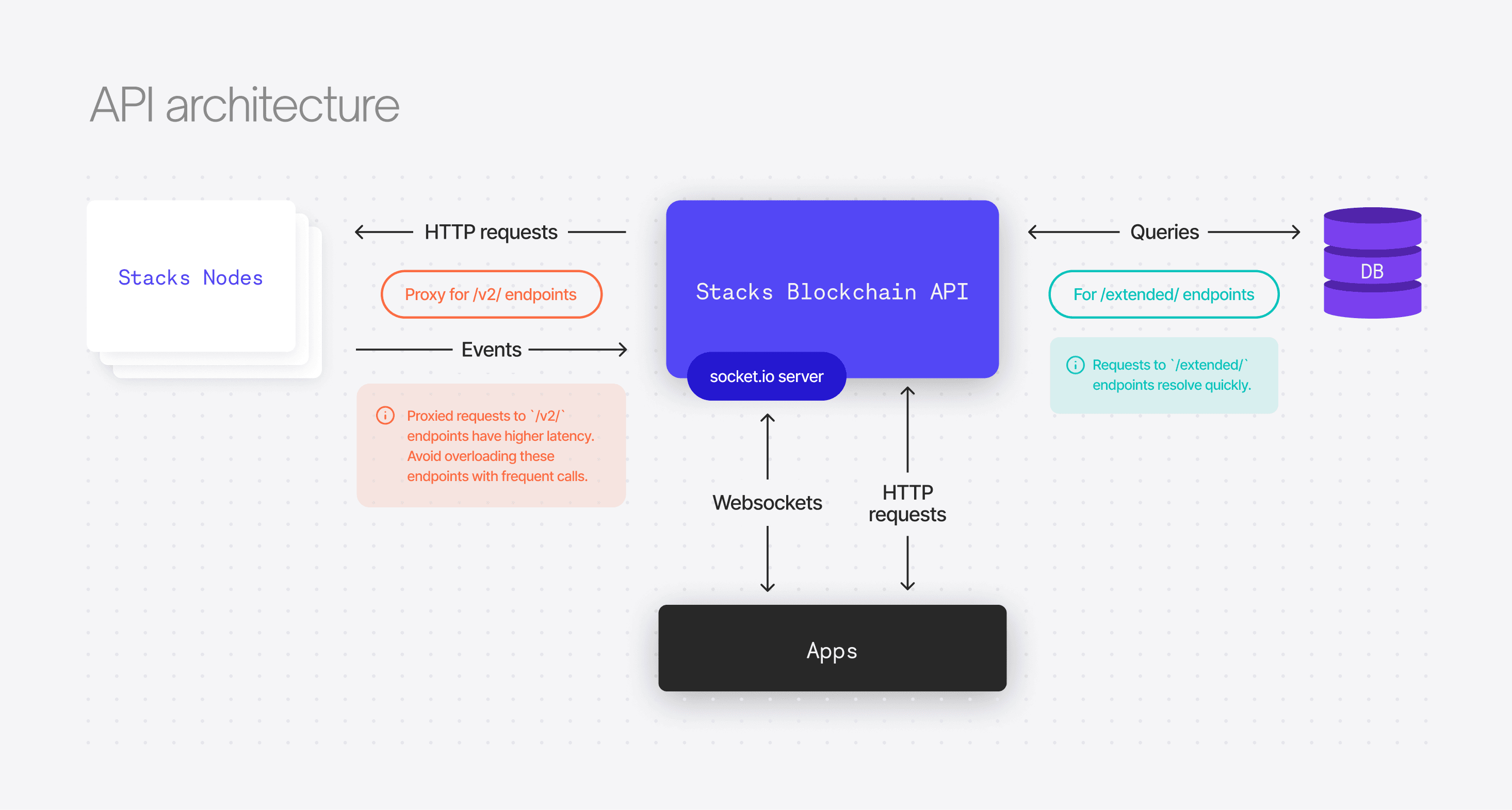
The stacks-node has its own minimal set of http endpoints referred to as RPC endpoints.
- The
stacks-blockchain-apiallows clients to access RPC endpoints by proxying requests to a load-balanced pool ofstacks-nodes. - For more details on RPC endpoints, see: RPC Endpoints Documentation
- Common RPC endpoints include:
POST /v2/transactions- Broadcast a transactionGET /v2/pox- Retrieve current Proof of Transfer (PoX) relevant informationPOST /v2/contracts/call-read/<contract>/<function>- Evaluate and return the result of calling a Clarity functionPOST /v2/fees/transaction- Evaluate a given transaction and provide transaction fee estimation dataGET /v2/accounts/<address>- Fetch the current nonce required for creating transactions
The Stacks Blockchain API implements additional endpoints that provide data unavailable directly from Stacks nodes due to various constraints.
- The
stacks-nodemay not persist certain data or may not serve it efficiently to many clients. For instance, while it can return the current STX balance of an account, it cannot provide a history of account transactions. - The API implements the Rosetta specification by Coinbase, an open standard designed to simplify blockchain deployment and interaction. More information can be found at Rosetta API.
- The API includes support for the Blockchain Naming System (BNS) endpoints. Details are available at BNS Documentation.
- For Express.js routes, see the directory
/src/api/routes.
The API creates an "event observer" http server which listens for events from a stacks-node "event emitter".
Events are HTTP POST requests containing:
- Blocks
- Transactions
Byproducts of executed transactions such as:
- Asset transfers
- Smart-contract log data
- Execution cost data
The API processes and stores these events as relational data in PostgreSQL. For the "event observer" code, see /src/event-stream.
All http endpoints and responses are defined in OpenAPI and JSON Schema.
- See
/docs/openapi.yaml - These are used to auto-generate the docs at https://hirosystems.github.io/stacks-blockchain-api/
- JSON Schemas are converted into TypeScript interfaces, which are used internally by the db controller module to transform SQL query results into the correct object shapes.
- OpenAPI and JSON Schemas are also used to generate a standalone @stacks/blockchain-api-client.
The easiest/quickest way to develop in this repo is using the VS Code debugger. It uses docker-compose to set up a stacks-node and Postgres instance.
Alternatively, you can run npm run dev:integrated which does the same thing but without a debugger.